Tin Mới
Executing Python Scripts through PowerShell: A Step-by-Step Guide
Running Python scripts from PowerShell is a powerful way to integrate Python capabilities into a Windows environment. Before diving in how to run a Python script from PowerShellit is important to ensure that Python is installed on your Windows computer.
Installing Python on Windows
If Python is not already installed, typing ‘python’ at the Command Prompt (CMD) will redirect you to the Microsoft Store, where you can download and install the latest version of Python.

Once installed, typing “python” in CMD will successfully launch the Python interpreter.
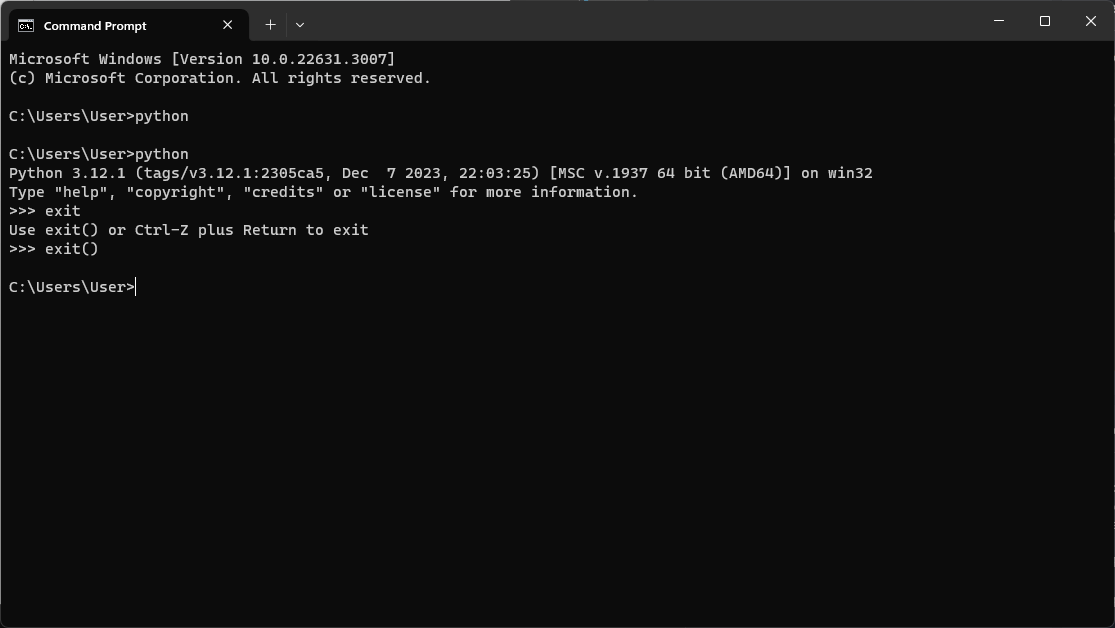

Creating a simple Python script
Let’s start by creating a basic Python script that takes a command line argument and prints it. Here is a simple example:
import sys
# Takes the first argument after the script name
input_arg = sys.argv[1]
print(f"Received argument: {input_arg}")
This script uses the `sys` module to access the command line arguments passed to the script. The script then prints the first argument (`sys.argv[1]`).
You can also check how to deploy and run a Python script on a Windows 10, 64-bit machine that doesn’t have Python installed.
Running Python script from PowerShell
To run this Python script from PowerShell, the paths to the Python executable and the script file must be specified correctly. Here’s how you can modify the provided PowerShell script for a Windows environment:
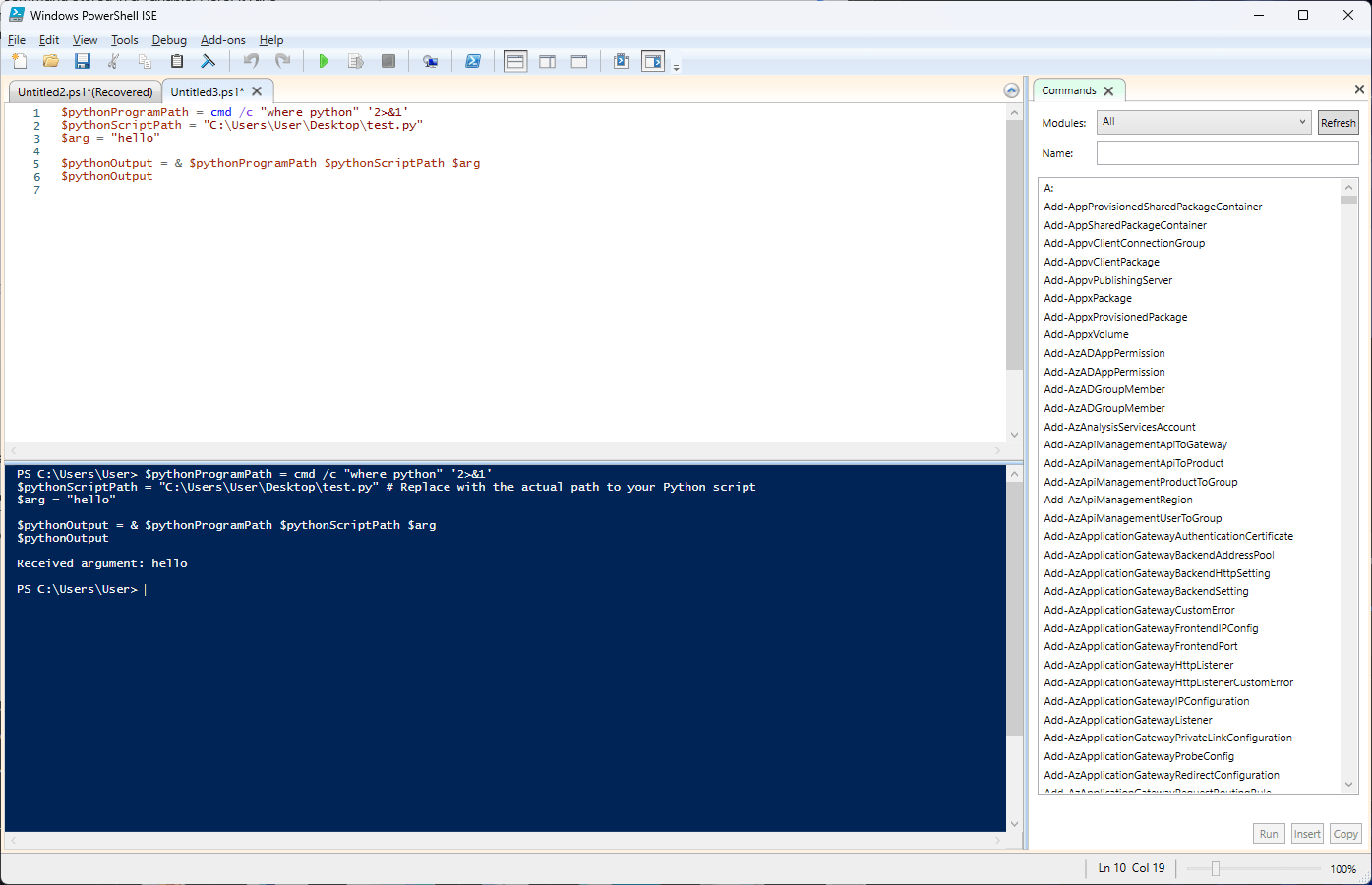
$pythonProgramPath = cmd /c "where python" '2>&1' $pythonScriptPath = "C:\Path\To\Script\main.py" $arg = "hello" $pythonOutput = & $pythonProgramPath $pythonScriptPath $arg $pythonOutput
To get the path of your Python installation is quite easy as it usually reflects either:
- C:\Python36
- C:\Users\(Your registered user)\AppData\Local\Programs\Python\Python36
To easily find where Python is installed, run the following command:
By defining the Python execution path dynamically with cmd /c “where python” ‘2>&1’we ensure that the correct Python location is used.
Then, `$pythonScriptPath` holds the full path to the Python script you want to run, “main.py”.
`$arg`, is a variable that stores the argument we want to pass to our Python script. In this example, it is the string “hello”. Remember that the script requires an argument to work correctly.
of `&` operator in PowerShell executes a command stored in a variable. Here, it executes Python with the script path and argument as parameters.
Output from Python script (print statement) is caught in `$pythonOutput` variable in PowerShell.
`$pythonOutput` display the output from the Python script in the PowerShell console.

CONCLUSION
Integrating Python scripts into PowerShell workflows allows you to leverage the extensive capabilities of Python in a Windows environment.
By setting the paths correctly and understanding how to pass arguments from PowerShell to Python, you can create powerful scripts and automation tools that combine the strengths of both languages. This approach is particularly useful for system administrators, developers and IT professionals looking to streamline their workflows and automate repetitive tasks.
Join our technical communityRaise your tech game! Subscribe to our blog for concise guides, expert insights and the latest trends in app packaging. Register now!



